Customs clearance is a pivotal aspect of global trade, serving as the gateway for goods to cross borders and access new markets. For shipping companies, whether engaged in maritime transport or air transport, a deep understanding of customs procedures is indispensable. These procedures act as the linchpin in facilitating smooth cross-border transactions, regardless of the company's size or mode of transport. It's the regulatory mechanism by which governments oversee and ensure compliance with various laws, tariffs, and trade agreements.
In today's interconnected landscape of international shipping, where shipping companies play a central role in global trade, adeptness in customs clearance procedures is more critical than ever. It transcends mere bureaucratic formalities, becoming a strategic imperative for shipping companies to enable the seamless movement of goods across borders and oceans.
This article aims to explore the customs clearance process, illuminating its significance and offering insights for shipping companies and businesses involved in import-export activities. By demystifying customs clearance, our goal is to equip readers with the knowledge and tools necessary to navigate international trade confidently and efficiently, whether dealing with sea shipments or air shipments.
The basics of customs clearance

Customs clearance is vital for both importing and exporting goods across borders. It serves several critical purposes, including ensuring the security of the supply chain, collecting duties and taxes, and enforcing trade regulations. Without proper customs clearance, goods cannot legally enter or exit a country, leading to delays, penalties, and potential disruptions to trade operations. Therefore, for shipping companies and businesses engaged in import-export activities, mastering the customs clearance process is imperative for conducting cross-border transactions seamlessly and efficiently.
Essential elements of customs clearance
The customs clearance process involves a series of steps designed to verify the legality, accuracy, and compliance of imported or exported goods. This process typically begins with the submission of documentation, including commercial invoices, packing lists, and certificates of origin, to customs authorities. Once the documentation is received, customs officials review and assess the information to determine the appropriate duties, taxes, and tariffs applicable to the goods. Subsequent steps may include physical inspections, where customs officials examine the goods to ensure they comply with regulatory requirements and are safe for import or export. Once all necessary checks are completed, customs clearance is granted, the shipments are released allowing the goods to proceed to their destination.
Another fundamental aspect of customs clearance is the Goods classification. Each item being imported or exported must be classified according to a standardized system, such as the Harmonized System (HS) code, which assigns a unique code to different products based on their characteristics. Proper goods classification is essential for determining the appropriate duties, taxes, and tariffs applicable to the goods, ensuring compliance with trade regulations, and facilitating smooth customs clearance processes.
Importance of Accurate Documentation and Proper Goods Classification
Accurate documentation and proper goods classification help prevent customs disputes and trade disputes between countries. By providing transparent and verifiable information about the goods, businesses can mitigate the risk of misunderstandings or disagreements with customs authorities, fostering smoother trade relations and facilitating cross-border transactions.
Incorrect or incomplete documentation can lead to delays, penalties, and even seizure of goods, disrupting trade operations and incurring additional costs for businesses.
How long does Customs Clearance take?
The timeframe required for customs clearance is subject to numerous factors. Typically, the process can be finalized within a short span of time, ranging from minutes to a few hours. Nevertheless, if essential documents are absent, goods necessitate inspection, or inquiries need resolution, the duration may substantially extend, sometimes spanning several days or even weeks. Throughout this period, the goods remain stationary at the border, awaiting clearance. Only upon the conclusion of all requisite inspections by customs authorities and the formal granting of clearance can the goods proceed with their journey across the border.
The most important shipping documents

Commercial Invoice
Among the indispensable documents for shipping your ocean freight is the Commercial Invoice. This essential document is issued by the seller (exporter) to the buyer (importer) and holds significant importance in the customs clearance process.
Packing List
When transporting ocean freight internationally, the Packing List serves as a comprehensive overview of the cargo delineated in the Commercial Invoice, it includes details on packaging and identifies markings and numbers on shipment boxes.
Export/Import Customs Declaration
Integral to international freight shipping, an Export or Import Customs Declaration delineates goods imported or exported. This declaration holds legal significance, signifying the intent to subject goods to specific customs procedures, facilitating customs clearance and aiding in duty or tax calculation.
Bill of Lading & Sea Waybill
The Bill of Lading, a meticulously detailed document, serves as a transportation contract, containing vital shipment details. It is an indispensable aspect of ocean freight, serving as evidence of goods received by the carrier from the shipper in satisfactory condition. Conversely, a Sea Waybill, although also a transport contract, is not indispensable for cargo delivery and serves solely as a cargo receipt, devoid of negotiability.
Certificates (Production, Vessel, Phytosanitary)
The requisite certificates, contingent upon cargo type, include:
- Production Certificate: Essential for goods using sustainable resources or approved methods, this certificate permits cargo shipment in or out of regulated regions.
- Vessel Certificate: Primarily verifying vessel ownership, it provides additional details such as vessel age and maintenance, typically required for Letter of Credit compliance.
- Phytosanitary Certificate: Certifies the absence of regulated pests in plants or plant products, ensuring conformity with importing country phytosanitary regulations.
Air or Rail Waybill
Depending on transport mode, an Air or Rail Waybill is issued. The Air Waybill, a non-negotiable document issued by an air carrier, acknowledges possession of the shipment, and serves as a receipt for the consignor. Conversely, a Rail Waybill, used for rail shipments, is prepared by the shipping agent or railway line, following shipper instructions.
Arrival Notice
The Arrival Notice alerts the consignee of cargo arrival, furnishing details such as commodity description, sailing particulars, destination customs charges, and ocean freight carrier contact information. It is issued by the ocean freight carrier's destination agent to pertinent parties mentioned on the Bill of Lading.
Certificate of Origin
Essential for determining goods' manufacturing country, the Certificate of Origin contains product, destination, and export country details, aiding import eligibility and duty assessment.
Importer Security Filing (ISF)
Required for ocean cargo imports into the United States, the Importer Security Filing mandates the submission of pertinent data to US customs and border protection 24 hours before sailing from the last origin port.
This ensures compliance with US customs regulations.
Letter of Credit
A primary payment mechanism in international trade, the Letter of Credit is irrevocable by default. It embodies a bank's promise on behalf of the importer to the exporter, stipulating a specified sum in an agreed currency and necessitating submission of requisite documents within a predetermined deadline. Additionally, it outlines goods description, quantity, technical details, and documentary requisites.
Understanding customs regulations
Now that we've established the fundamentals of customs clearance and covered essential shipping documents, let's delve deeper into the intricate world of customs regulations. In this section, we'll navigate through specific customs regulations and procedures that shipping companies and businesses engaged in import-export activities need to comply with for successful sea freight and air freight operations.
Import/Export Restrictions
Customs regulations impose various restrictions on the import and export of goods, aiming to protect national security, public health, and the environment. These restrictions can include prohibitions on specific items, such as weapons or hazardous materials, as well as quotas or licensing requirements for controlled substances or endangered species. It's important to note that import/export restrictions vary from country to country, and businesses must carefully review and comply with the regulations of each jurisdiction they operate in.
Duty Rates
Duty rates, also known as tariffs, are taxes imposed on imported goods by customs authorities. These rates can vary significantly depending on factors such as the type of goods, their country of origin, and any trade agreements in place. Understanding duty rates applicable to their products is essential for shipping companies and businesses to accurately calculate import costs and assess the financial implications of cross-border trade. It's worth noting that duty rates are country-specific and may change over time due to changes in trade policies or agreements.
Customs Valuation Methods
Customs authorities employ various methods to determine the value of imported goods for duty assessment purposes. Common valuation methods include transaction value, where the price paid or payable for the goods serves as the basis for valuation, and the deductive or computed value method, which calculates the value based on the goods' resale price. Comprehending these valuation methods is crucial for shipping companies and businesses to accurately declare the value of their imports and ensure compliance with customs regulations. It's important to remember that customs valuation methods may vary between countries and may impact the final import duties payable.
Compliance with Trade Agreements
Many countries participate in trade agreements or preferential trade arrangements aimed at promoting international trade and economic cooperation. These agreements often entail tariff concessions or preferential treatment for goods traded between member countries. However, accessing these benefits requires strict compliance with the rules of origin and other criteria specified in the agreements. Shipping companies and businesses must navigate these complex regulations to leverage the advantages offered by trade agreements and optimize their sea freight and air freight activities. Importantly, the terms of trade agreements are unique to each agreement and may differ from one country to another.
Simplifying customs clearance procedures
Navigating the customs clearance process can be complex, but there are practical tips and strategies that businesses can employ to streamline operations and ensure efficient cross-border trade. In this section, we'll explore some key strategies for simplifying customs clearance procedures, including the benefits of utilizing customs brokers or freight forwarders.
Utilize Freight Forwarders or Customs Brokers
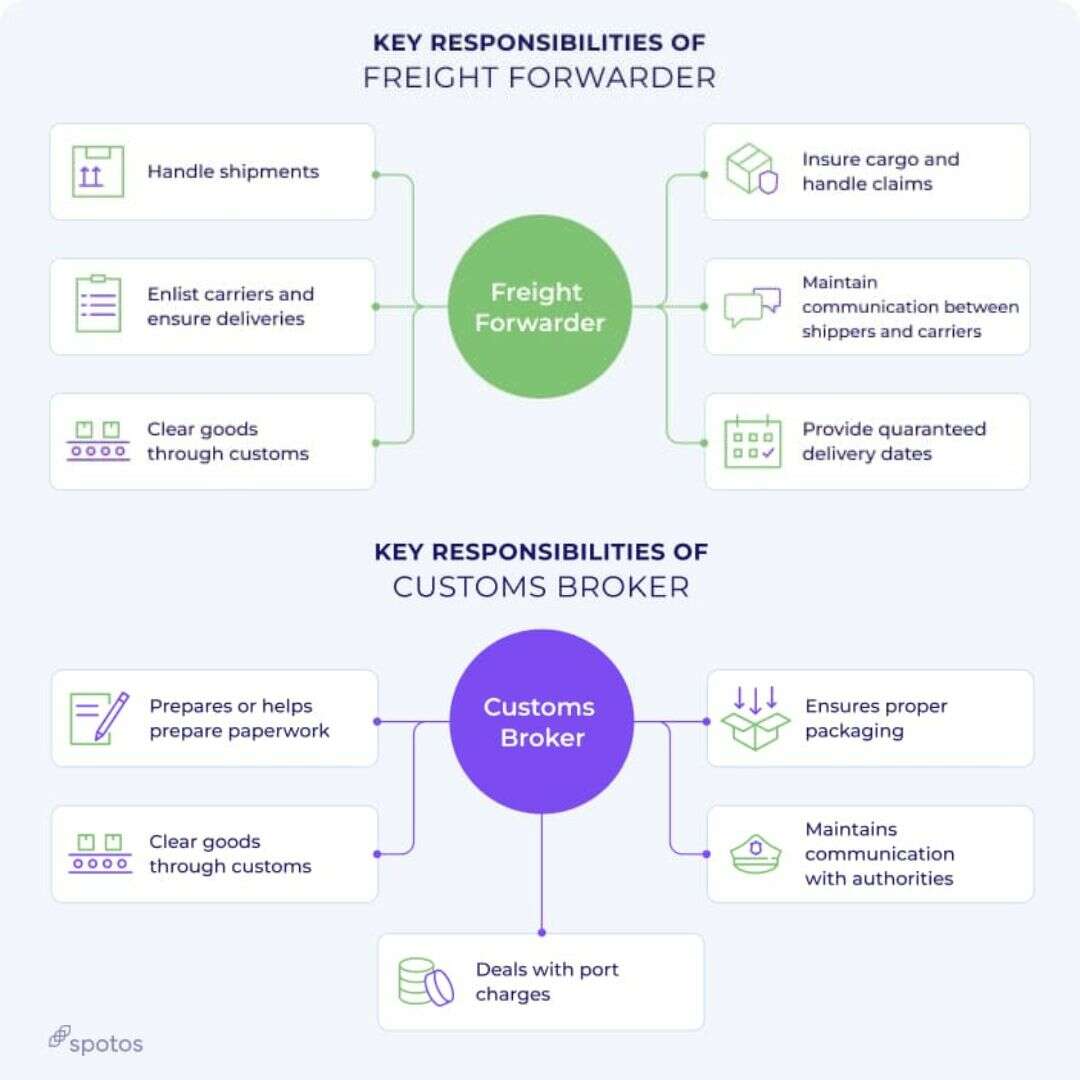
One of the most effective ways to simplify customs clearance procedures is by enlisting the services of experienced freight forwarders or customs brokers. These professionals specialize in customs regulations and procedures, helping businesses expedite the clearance process and avoid costly delays or errors. Customs brokers act as intermediaries between businesses and customs authorities, assisting with documentation preparation, customs filings, and compliance with regulatory requirements. Similarly, freight forwarders manage the logistical aspects of shipping, including customs clearance, transportation, and warehousing, providing end-to-end solutions for businesses engaged in import-export activities. By leveraging the expertise of customs brokers or freight forwarders, businesses can streamline customs clearance procedures, minimize risks, and focus on their core operations.


Maintain Accurate and Complete Documentation
Complete and accurate documentation is essential for smooth customs clearance. Businesses should ensure that all required paperwork, including commercial invoices, packing lists, certificates of origin, and customs declarations, is prepared correctly and submitted in a timely manner. Inaccurate or incomplete documentation can lead to delays, penalties, and disruptions to trade operations. By maintaining meticulous records and adhering to documentation requirements, businesses can expedite the clearance process and mitigate compliance risks.
Stay Informed and Up-to-Date
Customs regulations and procedures are constantly evolving, with new requirements, tariffs, and trade agreements being introduced regularly. To navigate these changes effectively, businesses must stay informed and up-to-date on the latest developments in customs law and policy. This includes monitoring changes in import/export regulations, tariff classifications, and trade compliance requirements. By staying informed, businesses can proactively address compliance issues, identify opportunities for optimization, and adapt their customs clearance strategies to changing market conditions.
Establish Strong Relationships with Customs Authorities
Building strong relationships with customs authorities can facilitate smoother customs clearance procedures and foster collaboration between businesses and regulatory agencies. By establishing open lines of communication and engaging constructively with customs officials, businesses can gain valuable insights into customs processes, address compliance issues more effectively, and expedite clearance times. Additionally, proactive engagement with customs authorities can help businesses resolve disputes, obtain regulatory guidance, and navigate complex customs regulations with greater confidence.
Conclusion
In conclusion, mastering customs clearance is essential for shipping companies and businesses in import-export operations, whether it involves sea or air shipments. Understanding key aspects like essential documents, import/export regulations, duty rates, and compliance with trade agreements is crucial for seamless cross-border trade.
Utilizing customs brokers or freight forwarders, maintaining accurate documentation, staying updated on regulatory changes, and fostering relationships with customs authorities are vital strategies for streamlining customs clearance.
As the global marketplace evolves, staying informed and embracing innovation will be key to unlocking new opportunities and driving growth in international trade. By adopting proactive approaches and adhering to best practices, businesses can navigate customs clearance confidently and succeed in the global marketplace.